Using Integrated Windows Authentication in IIS
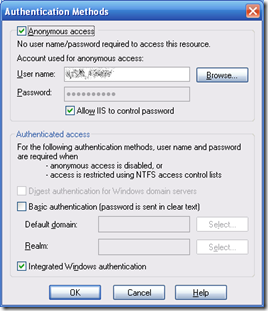
Many public facing web sites need to have special “admin” modes, or even completely different personalities for internal staff. One possible method of achieving this is to use the Integrated Windows Authentication in IIS which can be setup from the Directory Security tab of the IIS MMC snap in as shown here
If the anonymous access option is checked then anyone can access the site if not then the user’s windows credentials will be sent by the browser. This happens automatically when using IE. If you use Firefox then you will be prompted for your credentials each time, though you can white-list domain hosts to have your credentials send automatically.
Recently I came across an interesting problem with this configuration, the site I was trying to access would not recognise my Windows identity. I was using IE and it turned out that the fact that it usually automatically worked meant that I’d never really understood how it is configured in IE.
It appears that credentials are automatically passed to web sites where the domain of the web server and the domain of the machine with the browser are then same, this does make sense as its designed for intranets.
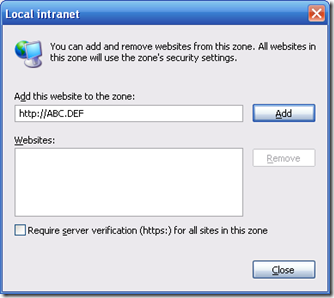
The site I was trying to access was of the form http://ABC.DEF whereas the domain of the machine with the browser was XYZ.ABC.DEF and because the domain names did not match my credentials were not being passed correctly. The solution was actually very easy, all I has to do was add the ABC.DEF into the Local Internet Zone in IE. It can be set from Internet Options > Security Tab > Local Intranet > Sites > Advanced
Please do be careful with adding domains into the Local Intranet as you are obviously lowering your security with regard to these domains and there are good technical security reasons to not just exchange your credentials with any host. In general only add domains that you trust.